Edge computing: the new face of the cloud
The Next Generation of Data Center and Cloud Architecture
You might have heard a lot about Cloud computing but what is this new term “Edge Computing”? How is it different from Cloud and why do we need another way of computing when we are still not done catching up with cloud computing?
In today’s article, we will figure out answers to these questions in-depth and will go through the story of this new chapter of Computing and how it’s evolving.
Let’s get started
Computing evolved at the same time when the Internet was catching up and has gone through various phases of computing.
Early computing: Centralized applications running in an isolated computer
Personal computing: Decentralized applications running locally
Cloud computing: Centralized applications running in data centers
Edge computing: Centralized applications running close to users, either on the device itself or on the network edge
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing refers to computing power made available in the cloud across the globe from a central server and database. It’s one step ahead from the previous computing era limited to personal computing resources only available to specific locations which incurred costly hardware costs. Cloud computing democratized computing resources to a global audience and we saw a rise in the number of cloud providers like AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud.
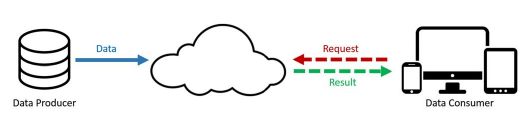
With the advent of cloud computing, computing resources were democratized from being a central resource to a global resource that can be accessed from across the globe.
The idea behind the cloud was to store all data in one place for complex computing to take place in its most favorable environmental conditions for a data center to function optimally.
However, it’s important to understand that:
Edge doesn't replace cloud computing. Edge computing is an add on to the cloud computing structure.
Now let’s understand what’s edge computing
Edge computing
If we go by literal meaning of the word “Edge” it refers to the immediate boundary or periphery of an object, now adding computing with edge means, computing power made available right at the source of data.
It’s a form of computing made available at or near the source of data. Edge brings cloud close to your home and regional areas instead of data traveling from your device to google’s data center and then back to your device.
Edge computing is a modern version of data center and cloud architecture enhanced with real-time data transfer made locally available to the devices. It helps in the improved user experience of IoT applications. Edge computing completely eliminates the bandwidth and throughput issues caused by long-distance between users and applications.
Though you can’t say edge is a completely new thing in itself, rather it’s an alternative approach to the cloud. In simple words-
Edge is cloud computing made available locally at the edge of the network.
Why Edge Computing
Consumers are the biggest producer of data, and with smart devices build with IoT and AI-enabled features this data is only going to increase exponentially, leading to a sharp increase in the total amount of world data.
Data doesn’t come free, it needs bandwidth and energy to travel. And the rate at which we are generating data is not sustainable. We need an alternative to lighten up data overload and diminish problems caused by excess data.
A typical data undergo various costs while data processing, data collection, data transmission, data storage, data security, and many other costs. This data is used to enable a seamless YouTube and Netflix recommendation engine to work. In every real-time business, there is a data channel working behind the scenes at every touchpoint to make your experience seamless with that application. IoT is a big jump in a real-time application where edge computing provides an effective middle way through this conundrum of data transmission.
The prerequisite to use cloud computing is access to a high bandwidth network to transfer data on the web, which diminishes with edge computing.
What is “Edge computing” and what isn’t edge
Edge is a bit of a fuzzy term. Assume a use case of a user’s computer or the processor inside an IoT camera. The processor can be considered the network edge, but the user’s router, ISP, or local edge server are also considered the edge. But none of them defines the kind of work done by an edge-enabled device.
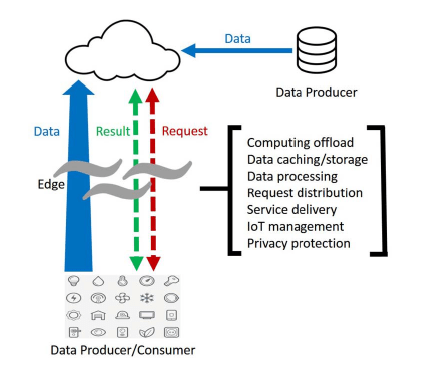
Edge refers to a local network edge where the device, or the local network containing the device, communicates with the Internet.
The important takeaway is that the edge of the network is geographically close to the device, unlike origin servers and cloud servers, which can be very far from the devices they communicate with.
Immediate benefits for a business to shift towards edge-based solutions :
Improve data security and privacy of every individual user in the network.
Excellent user experience with quick real-time response engines built-in IoT applications.
Gain a competitive advantage in fast-growing industries.
Get along with regional data compliance laws such as the one imposed in the UK and its regions.
Increased adoption and usage of latency-sensitive apps with restricted connectivity.
Scale easily by reducing the amount of data generated for real-time computing and analytics which is almost 75% as per the Gartner report.
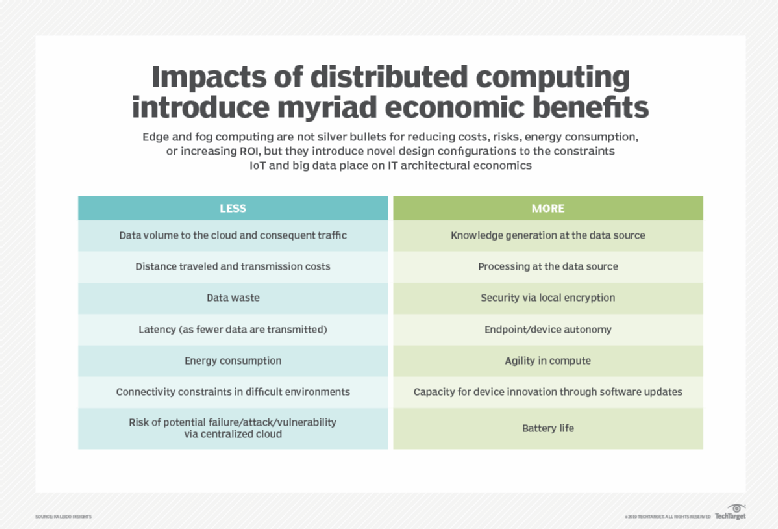
Why the shift to edge computing
Moving to compute resources to the edge of a device needs a huge infrastructure to work successfully. It needs change in data architectures and distribution which in itself require lots of capital and investment of time and money. But still, its positive side is forcing many enterprises to adopt it fast.
Organizations waste an estimated $62 billion a year paying for extra data storage capacity that they don't need, according to a recent study by Stanford researcher Jonathan Koomey. Data centers in US accounts for 2% the total U.S. energy consumption in 2014, according to a study by the U.S. government on data center energy use.
About 10% of organizational data resides outside a traditional data center or cloud, but Gartner predicts that this number will increase to 75% within just five years.

Reasons to shift from cloud to edge
Costs associated with centralized data processing and data storage.
Better performance, reliability, and security to meet the urgent needs of an organization.
Exponential data growth also compounds the demand for real-time data for longer-term strategic decision-making, which decreases the financial losses in the future.
Reduced volume of data sent to the cloud translates to less latency, cost, and traffic.
Processing data locally reduces connectivity constraints in remote and difficult environments - hence rendering these places for more viable real-time and even mission-critical applications.
Improved security and privacy of data. In the cloud, a centralized server invites more risk from malicious actors or network failure. While in Edge Computing this risk gets reduced to the individual network edge.
💡The average cost of a data breach was $3.86 million in 2018
To summarize edge improves the major pain points of a business
1. Product experience and user satisfaction
2. Cost of running a business
These are two major objectives of a business and there is no reason why a business in real-time services will not go for edge computing. Many IoT applications create a bunch of data that is useless. For example, data that is just a case of stating everything is OK, or the system needs Reboot doesn't need to traverse the network, but many IoT devices don't have the built-in intelligence to know this and hence add on useless data over the web.
In fact, an IoT environment can’t be fully managed optimally through a 100% cloud-based platform. There arises a problem of data storage, transport of a huge chunk of useless data, data latency, and many other costs. And here comes the savior to tackle all these hard problems 🥁🥁🥁.
Edge computing😎
Superpowers of edge computing
So far we have seen many great points about “Edge Computing” and why companies are going for it. Let’s delve deeper into what are those great features that give an edge to “Edge Computing” over traditional cloud computing.
1. Cost Saving
It minimize bandwidth use and server resources. Bandwidth and cloud resources are finite and cost money.
2. Data latency
Edge significantly reduce data latency. It brings data center close to the devices and completely remove a huge lag that came while the data was flowing through a big data transport system.
3. Security & Privacy
The edge is defined in such a manner that the data collected at the user remains with the user and the final result of the whole processing of data goes back to the data center. This makes the edge a go-to option to keep security and privacy at the front.
Privacy features of an iPhone are well accepted as an example of edge computing. What it does is encrypt and store the biometric information on the device, and offloads a ton of security concerns from the centralized cloud to its users devices.
For security reasons the management side of edge computing is very crucial simply because the definition of security is in the hands of management, if it goes wrong the whole security is at stake.
4. Performance
In edge the work is done right where the data is generated - that's can be a set of cameras, light bulbs, an autonomous vehicle, or a smart city. This improves the performance metric for real-time business insights, equipment maintenance predictions, and other critical actions.
Gartner predicts that by 2025, 75% of enterprise-generated data will be created outside central data centers. How to transfer so much data in time critical situations is itself an incredible problem to solve for, given the global internet is already subject to data congestion and overload from the data generated in last two years.
Disadvantages’ of edge computing
1. Security Risk
Edge brings more "smart" devices into the user’s self, such as edge servers, IoT devices that have robust built-in computers. But it also comes with a downside of new opportunities for malicious attackers to compromise individual devices and hack private data.
2. Hardware Costs
Another drawback with edge computing is that it needs more local hardware resources.
For Example - An IoT camera needs a built-in computer to send its raw video data to a web server, it also requires a much more sophisticated computer with more processing power in order to run its own motion-detection algorithms.
💡 One ray of hope here is costs of the hardware are dropping consistently and make it cheaper to build smart devices with inbuilt hardware resources.
3. Complex Network Architecture
Edge computing moves all the data analysis and computing away from a central IT platform towards where the data is created to minimize data movement, improve performance and place a certain level of intelligence close to IoT devices.
These fancy features need a strong technology stack to back them up. It requires advance planning and resource investment ahead of time. Network architects play a pivotal role to build scalable network architecture for edge computing.
This puts a special computing unit, known as an edge device within the environment to capture, manipulate, analyze and make decisions on what actions should be carried out.
A good idea in theory, but problems arise in practice.
Conclusion
Edge Computing seems to solve all the big problems with the current computing and data overload crisis and cloud decentralization is a good way to go about it. Real-time IoT-based applications bring the best of both the cloud and IoT world to create a better product experience. The simple logic behind edge is, it stores all the data that a smart device needs to work efficiently and compute it in real-time in the same device, and then sends the results of the analysis to the main server.
Also, there isn’t much growth left in the cloud space. Almost everything that can be centralized has been centralized. New opportunities for the “cloud” now lie at the “edge”. Edge brings a new avenue in the era of computing which holds the promise to grow at an exponential rate with the advancements in IoT and 5G technologies.
With these super-advanced features of Edge Computing, the future looks safe and brighter with Edge computing.
That’s it for this week.
Leave your thoughts on what do think of the revolutionary features of edge computing and how it’s going to change your world.
If you are new here, Do subscribe for more insights on new technologies and trends every week.
Wanna bring one of your friends to get into a good discussion on Edge Computing, Share this with a friend you want to grow with…
Until next week
Stay hungry, Stay curious
Sneha Prajapati




Sneha Prajapati's article is a beacon of clarity in the ever-evolving landscape of computing. The journey from centralized to edge computing is artfully illuminated, making tech concepts a breeze for readers. The analogy of Edge as the 'periphery of an object' brilliantly demystifies this cutting-edge tech, bringing cloud computing closer to home and regional spaces. The piece's conversational tone transforms complex topics into an engaging narrative, making it a tech-read delight! The detailed exploration of Edge's benefits, from cost savings to enhanced security, cements its pivotal role in the tech realm. A heartfelt thank you to Sneha Prajapati for unraveling the wonders of Edge Computing, making tech enlightenment accessible!
• For similar topics, read this article: https://www.techtopia5.com/2023/08/edge-computing-technology.html
• Also follow: https://www.techtopia5.com/